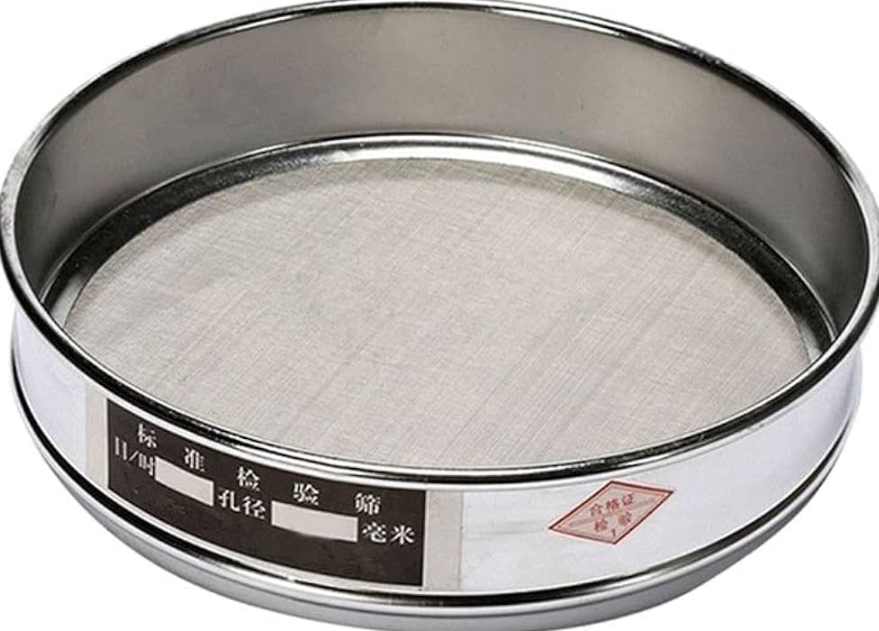
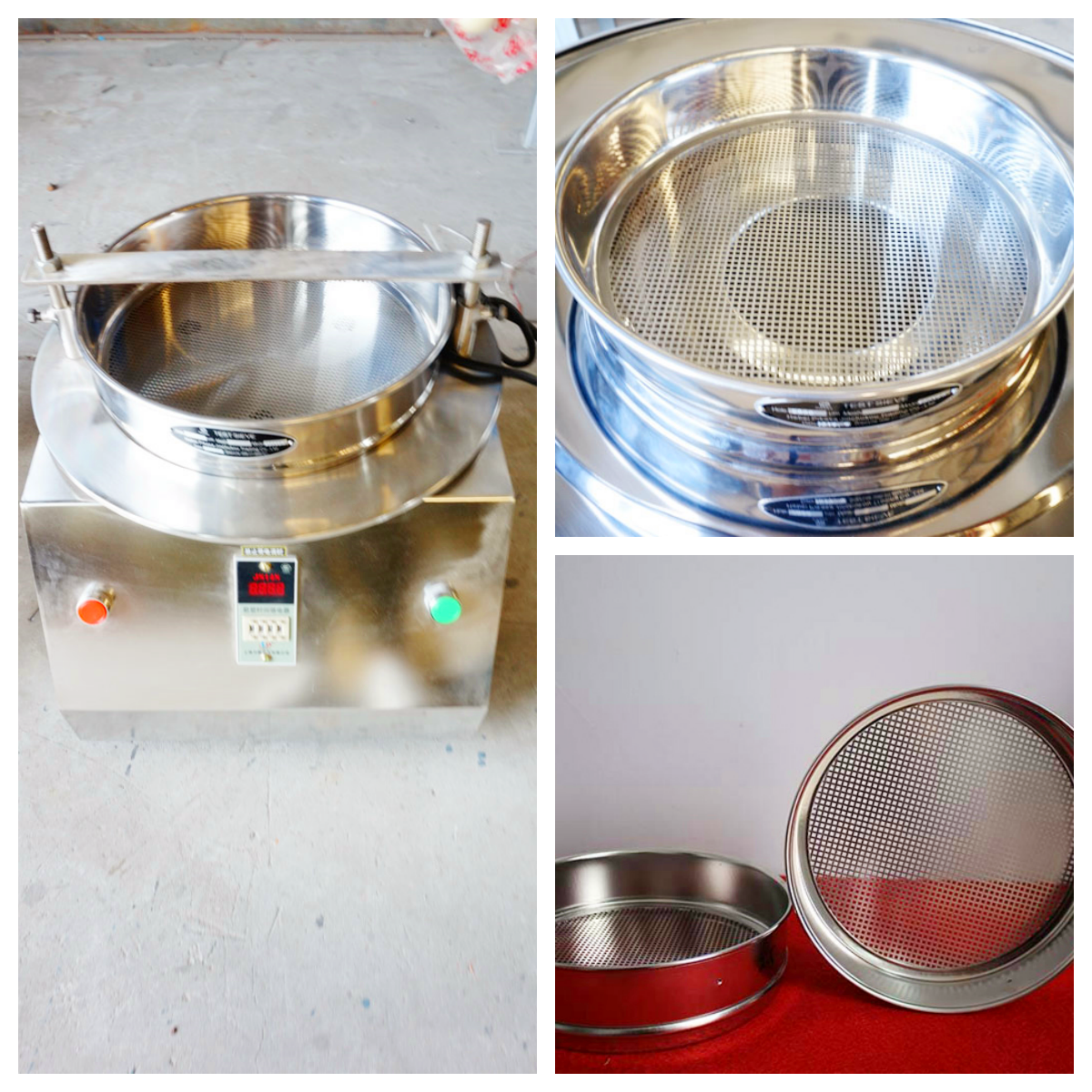
Test sieve vs. analytical sieve
Tuesday July-15 2025 15:09:32
Test sieve and analytical sieve are two kinds of mechanical equipment that often appear in the field of granular material screening. The two have similarities, but the focus and application scenarios are different.

Test sieve is a standard screening tool for particle size distribution testing of granular materials. It is mainly used for screening tests of granular materials in laboratories or on-site to obtain the particle size composition of the materials.
Analysis sieve usually refers to a sieve used for fine particle size analysis, emphasizing its screening accuracy and screening efficiency. The main purpose of the analytical sieve is to obtain the detailed particle size distribution of granular materials. It is often used as a test sieve or a higher standard sieve.
Comparison of size between Test sieve and analytical sieve
Test sieve mesh size
|
mesh size |
Standard mesh |
mesh size |
Standard mesh |
|
4.75mm |
4 mesh |
0.355mm |
45 mesh |
|
4.00mm |
5 mesh |
0.300mm |
50 mesh |
|
3.35mm |
6 mesh |
0.250mm |
60 mesh |
|
2.80mm |
7 mesh |
0.212mm |
70 mesh |
|
2.36mm |
8 mesh |
0.180mm |
80 mesh |
|
2.00mm |
10 mesh |
0.150mm |
100 mesh |
|
1.70mm |
12 mesh |
0.125mm |
120 mesh |
|
1.40mm |
14 mesh |
0.106mm |
140 mesh |
|
1.18mm |
16 mesh |
0.090mm |
170 mesh |
|
1.00mm |
18 mesh |
0.0750mm |
200 mesh |
|
0.850mm |
20 mesh |
0.0630mm |
230 mesh |
|
0.710mm |
25 mesh |
0.0530mm |
770 mesh |
|
0.600mm |
30 mesh |
0.0450mm |
325 mesh |
|
0.500mm |
35 mesh |
0.0374mm |
400 mesh |
Analytical sieve mesh size
|
No. |
Type |
Mesh(mm) |
No. |
Type |
Mesh(mm) |
|
1 |
8# |
2.360 |
15 |
70# |
0.212 |
|
2 |
10# |
2.000 |
16 |
80# |
0.180 |
|
3 |
12# |
1.700 |
17 |
100# |
0.150 |
|
4 |
14# |
1.400 |
18 |
120# |
0.125 |
|
5 |
16# |
1.180 |
19 |
140# |
0.106 |
|
6 |
18# |
1.000 |
20 |
170# |
0.09 |
|
7 |
20# |
0.850 |
21 |
200# |
0.075 |
|
8 |
25# |
0.710 |
22 |
230# |
0.063 |
|
9 |
30# |
0.600 |
23 |
270# |
0.053 |
|
10 |
35# |
0.500 |
24 |
325# |
0.045 |
|
11 |
40# |
0.425 |
25 |
400# |
0.038 |
|
12 |
45# |
0.355 |
26 |
500# |
0.028 |
|
13 |
50# |
0.300 |
27 |
>500# |
<0.028 |
|
14 |
60# |
0.250 |
|
|
|
What is the working principle of test sieves and analytical sieves?
Both test sieves and analytical sieves rely on the combination of sieve mesh aperture and mechanical vibration to achieve particle classification, but they have different focuses on principle execution. The core is to use the gradient distribution of sieve holes to separate materials by particle size, ensuring the accuracy of particle size analysis.
Basic principle: The material is placed on the top sieve frame with the largest aperture. Under the action of vibration (mechanical vibration or manual shaking), the material is evenly dispersed on the sieve surface. Particles smaller than the sieve hole fall into the next layer of sieve frame with smaller aperture, while particles larger than the sieve hole remain, realizing step-by-step classification from coarse to fine.
Principle differences: Test sieves focus on stable vibration intensity to meet routine screening needs, with vibration parameters (frequency, amplitude) set to adapt to batch material testing; Analytical sieves emphasize precise control of vibration uniformity, reducing particle blocking and agglomeration through optimized vibration modes (such as vertical micro-vibration), ensuring the accuracy of fine particle analysis.

Specifications of Test Sieve
|
Serial Number |
Name |
Unit |
Date |
|
|
1 |
Standard sieve body |
layer |
8 |
|
|
2 |
Screen diameter |
mm |
φ200φ100φ75 |
|
|
3 |
Screening size |
mm |
0.038-3 |
|
|
4 |
Noise |
dB |
≤50 |
|
|
5 |
Feeding amount (one time) |
g |
≤200 |
|
|
6 |
Amplitude |
mm |
≤5 |
|
|
7 |
Motor |
voltage |
V |
|
|
Rotating speed |
r/min |
1420 |
||
|
Power |
KW |
0.125 |
||
|
8 |
Dimensions |
mm |
360×300×736 |
|
|
9 |
Machine quality |
kg |
25 |
|
Specifications of Test Analytical Sieve
|
serial number |
name |
单位 |
参数 |
|
01 |
Screen frame |
层 |
1~8 |
|
02 |
Screen frame diameter |
mm |
Φ200 |
|
03 |
Screening size |
mm |
0.025~3 |
|
04 |
noise |
dB |
less than 50 |
|
05 |
amplitude |
mm |
0~3 |
|
06 |
vibration frequency |
times/min |
1440 |
|
07 |
Dimensions |
length width height |
350:350:300+N*50 |
|
08 |
power supply |
V;HZ |
220;50 |
|
09 |
Total Weight |
Kg |
36 |
|
10 |
vibration motor |
power |
0.12KW |
What are the specific application scenarios of test sieves and analytical sieves?

Test sieves are mainly used in laboratories or production sites for material classification, screening or quality control. The application range is wide, including particle classification in the building materials, chemical, mining, food, pharmaceutical and other industries. It is often used for rough screening or industrial use, and the accuracy requirements are relatively low.
Analytical sieves are designed for precise particle size analysis in laboratories and are widely used in scientific research, quality inspection and other fields. They are often used to determine the particle size distribution of fine particles (such as powders and microparticles), and high accuracy is required. Typical applications include soil analysis, powder research, chemical particle size detection, etc.
Main differences
|
Aspects |
Test sieve |
Analysis sieve |
|
Picture |
|
|
|
Main functions |
Conventional screening test of granular materials |
Fine particle size analysis, focusing on screening accuracy and repeatability |
|
Screening particle size |
0.038-3 mm (covering coarse particles to fine powder) |
0.03-2 mm (focusing on fine particle analysis) |
|
Screen accuracy |
Generally meets basic standards, wider aperture |
Higher accuracy, strict control of aperture size |
|
Usage scenarios |
Construction, mining and other on-site and laboratory routine testing |
Laboratory detailed particle size distribution analysis, scientific research purposes |
|
Matching equipment |
Can be screened manually or used with mechanical vibrating screen |
Mostly used with standard vibrating screen instruments |
In most cases, test sieves and analytical sieves refer to the same thing-high-precision sieves for precise particle size analysis in laboratories. The main difference between them lies in the emphasis of the words used, not the essential differences in the products themselves. When you buy or use it, it is more important to pay attention to whether the sieve meets the relevant standards and whether its technical parameters such as sieve hole size and material meet your specific application needs.











