What is a Standard soil sieve size
Monday July-14 2025 17:10:15
What is a standard soil sieve?
Standard soil sieve size is an experimental equipment used to screen soil samples and grade particle sizes. It is widely used in geology, agriculture, construction and environmental monitoring. The size and structure of the sieve must meet certain standards.

According to the aperture, standard soil sieves can be divided into coarse sieves (round holes) and fine sieves (square holes). The apertures of coarse sieves commonly used in geotechnical tests are generally 100mm, 80mm, 60mm, 40mm, 20mm, 10mm, 5mm, and 2mm. The equivalent aperture of fine screen (square hole) is generally 2.0mm, 1.0mm, 0.5mm, 0.25mm, 0.10mm, 0.075mm.
According to the diameter of the screen frame, it can be divided into φ200mm, φ300mm and φ400mm.
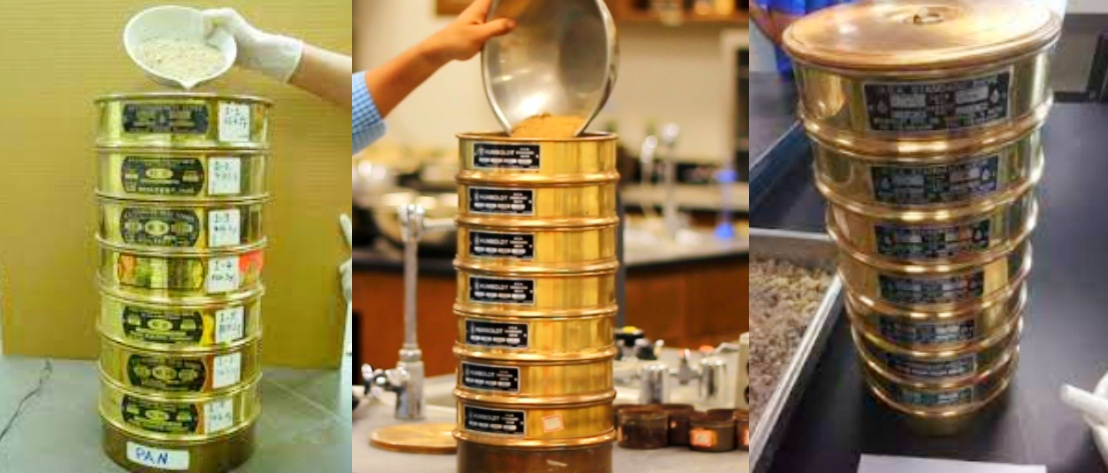
φ200mm: Usually there are 11 pieces/set + bottom cover, the screen hole size includes 0.074mm, 0.25mm, 0.5mm, 1.0mm, 2.0mm, 5mm, 10mm, 20mm, 40mm, 60mm, etc.
φ300mm: The mesh range is 0.074mm-60mm, such as the new standard soil screen (∮300, 10+1 section), its specifications are 0.075mm, 0.25mm, 0.5mm, 1mm, 2mm, 5mm, 10mm, 20mm, 40mm, 60mm.
φ400mm: Size specification is between 0.074mm-60mm.
How are Standard Soil Sieves Classified?
Standard soil sieves can be classified based on multiple dimensions, including aperture, sieve frame diameter, and material, each corresponding to specific application scenarios.
Classification by Aperture:Standard soil sieves are categorized by aperture into coarse sieves with round holes and fine sieves with square holes. Coarse sieves, used in geotechnical tests, have common sizes ranging from 100mm down to 2mm. Fine sieves, suitable for classifying fine-grained soil, feature equivalent apertures like 2.0mm, 1.0mm, and 0.075mm.
Classification by Sieve Frame Diameter:Based on sieve frame diameter, there are three main sizes. The φ200mm set usually contains 11 pieces + bottom cover, covering sizes from 0.074mm to 60mm. The φ300mm sieve offers a 0.074mm-60mm mesh range, with configurations like the new standard 10+1 section set. The φ400mm sieve maintains the same 0.074mm-60mm size specification range.
Classification by Material:The materials of sieve frames and screens affect their suitability. Sieve frames are made from stainless steel, copper, or aluminum alloy, with stainless steel being popular for its corrosion resistance. Screens are constructed from materials like stainless steel wire mesh or brass wire mesh, selected according to soil type—for example, stainless steel is used for acidic soil to prevent rust.
Metric and U.S. Standard Sieve Sizes Table
| ASTM E11 | ISO 565/3310-1 | |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Alternate | Size |
| 100.0mm | 4in | - |
| 90.0mm | 3 1/2in | - |
| 75.0mm | 3in | - |
| 63.0mm | 2 1/2in | 63.0mm |
| - | - | 56.0mm |
| 53.0mm | 2.12in | 53.0mm |
| 50.0mm | 2in | 50.0mm |
| 45.0mm | 1 3/4in | 45.0mm |
| - | - | 40.0mm |
| 37.5mm | 1 1/2in | 37.5mm |
| - | - | 35.5mm |
| 31.5mm | 1 1/4in | 31.5mm |
| - | - | 28.0mm |
| 26.5mm | 1.06in | 26.5mm |
| 25.0mm | 1in | 25.0mm |
| 22.4mm | 7/8in | 22.4mm |
| - | - | 20.0mm |
| 19.0mm | 3/4in | 19.0mm |
| 18.0mm | - | 18.0mm |
| 16.0mm | 5/8in | 16.0mm |
| - | - | 14.0mm |
| 13.2mm | 0.530in | 13.2mm |
| 12.5mm | 1/2in | 12.5mm |
| 11.2mm | 7/16in | 11.2mm |
| - | - | 10.0mm |
| 9.5mm | 3/8in | 9.5mm |
| - | - | 9.0mm |
| 8.0mm | 5/16in | 8.0mm |
| - | - | 7.1mm |
| 6.7mm | 0.265in | 6.7mm |
| 6.3mm | 1/4in | 6.3mm |
| 5.6mm | No. 3 1/2 | 5.6mm |
| - | - | 5.0mm |
| 4.75mm | No.4 | 4.75mm |
| - | - | 4.50mm |
| 4.00mm | No.5 | 4.00mm |
| 3.55mm | - | 3.55mm |
| 3.35mm | No.6 | 3.35mm |
| - | 1/8in* | - |
| 3.15mm | - | 3.15mm |
| 2.80mm | No.7 | 2.80mm |
| - | - | 2.50mm |
| 2.36mm | No.8 | 2.36mm |
| 2.00mm | No.10 | 2.00mm |
| - | - | 1.80mm |
| 1.70mm | No.12 | 1.70mm |
| - | - | 1.60mm |
| 1.40mm | No.14 | 1.40mm |
| - | - | 1.25mm |
| 1.18mm | No.16 | 1.18mm |
| - | - | 1.12mm |
| 1.00mm | No.18 | 1.00mm |
| - | - | 900μm |
| 850μm | No.20 | 850μm |
| - | - | 800μm |
| 710μm | No.25 | 710μm |
| - | - | 630μm |
| 600μm | No.30 | 600μm |
| - | - | 560μm |
| 500μm | No.35 | 500μm |
| - | - | 450μm |
| 425μm | No.40 | 425μm |
| - | - | 400μm |
| 355μm | No.45 | 355μm |
| - | - | 315μm |
| 300μm | No.50 | 300μm |
| - | - | 280μm |
| 250μm | No.60 | 250μm |
| - | - | 224μm |
| 212μm | No.70 | 212μm |
| - | - | 200μm |
| 180μm | No.80 | 180μm |
| - | - | 160μm |
| 150μm | No.100 | 150μm |
| - | - | 140μm |
| 125μm | No.120 | 125μm |
| - | - | 112μm |
| 106μm | No.140 | 106μm |
| - | - | 100μm |
| 90μm | No.170 | 90μm |
| - | - | 80μm |
| 75μm | No.200 | 75μm |
| - | - | 71μm |
| 63μm | No.230 | 63μm |
| - | - | 56μm |
| 53μm | No.270 | 53μm |
| - | - | 50μm |
| 45μm | No.325 | 45μm |
| - | - | 40μm |
| 38μm | No.400 | 38μm |
| - | - | 36μm |
| 32μm | No.450 | 32μm |
| 25μm | No.500 | 25μm |
| 20μm | No.635 | 20μm |
Common standard soil sieve size table (expressed in sieve hole size/aperture)

|
Mesh number (Mesh) |
Sieve hole size (mm) |
Remarks |
|
2 |
8.00 |
Boundary between gravel and coarse sand |
|
4 |
4.75 |
Upper limit of coarse sand |
|
10 |
2.00 |
Boundary between medium sand and coarse sand |
|
20 |
0.85 |
Upper limit of medium sand |
|
40 |
0.425 |
Boundary between fine sand and medium sand |
|
60 |
0.25 |
Upper limit of silt sand |
|
100 |
0.15 |
Silt sand subdivision |
|
200 |
0.075 |
Boundary between clay and silt sand |
|
300 |
0.053 |
Ultrafine powder |
|
325 |
0.045 |
For laboratory fine screening |
Note: "Mesh number" refers to the number of holes per inch on the sieve, which is used to describe the coarseness of the sieve. The commonly used sieve holes in soil analysis are: 2mm, 0.85mm, 0.425mm, 0.25mm, 0.075mm, etc.
| Testing Sieve Specification | ||
| Sieve Material | Brass, AISI304/316/316L, galvanized, etc. | |
| Technology | Woven | |
| Standard | ASTM E11-09 ISO3310-1 | |
| Sieve Diameter | 3" 6" 8" 10" 12" 200mm 300mm | |
| Frame | Material | Brass, stainless steel, etc. |
| Height (full) | 1-3/4'' -- 2-5/8'' | |
| Aperture shape | Square | |
| Mesh opening / Aperture | 5--500mesh 10--200μm | |
Structural dimensions (external dimensions) of standard soil sieve

|
Sieve frame diameter |
height (mm) |
material |
remarks |
|
200mm |
50 or 75 |
stainless steel/copper/galvanized |
common laboratory dimensions |
|
300mm |
75 or 100 |
stainless steel |
commonly used in engineering and geotechnical engineering |
|
450mm |
100 or 200 |
stainless steel |
used for large-scale screening |
Structural specifications of soil sieve
|
Project |
common specifications |
description |
|
Sieve frame diameter |
200mm/300mm/450mm |
most commonly used is 200mm (laboratory) |
|
Sieve frame height |
50mm (middle frame)/75m m (height frame) |
determines the screen loading amount |
|
Screen material |
stainless steel wire mesh, brass wire mesh, galvanized wire mesh, etc. |
stainless steel is the most common |
|
Screen frame material |
stainless steel, brass, aluminum alloy |
welded or clamped structure with screen |
|
Structural form |
integral welding/snap-on type |
ensure sealing and screening accuracy |
Soil sieve is an important tool for soil particle classification and screening. It has key uses in many fields. By screening soil particles of different particle sizes, the mechanical composition of the soil (such as the proportion of sand particles, silt particles, and clay particles) is analyzed, and then the porosity, permeability, water retention and other physical properties of the soil are studied. For example, in the classification of soil texture (such as the division of sand, loam, and clay), the soil type needs to be determined based on the screening results.

The sieved soil particles can be used to study the distribution of soil aggregates, evaluate the stability of soil structure, and provide data support for research on soil erosion and fertility maintenance. In studies on pollutant migration and soil remediation, screening soils of different particle sizes can analyze the adsorption and distribution of pollutants in different particles, such as the enrichment of heavy metals in fine-grained soil.
What are the applications of standard soil sieve?
Standard soil sieves are essential tools across diverse fields, enabling precise particle size analysis that informs critical decision-making processes. From engineering to environmental studies, their use helps ensure accuracy, safety, and efficiency.
Geological and Geotechnical Engineering:Analyze soil particle size distribution to classify soil types (e.g., sand, loam) and evaluate bearing capacity for foundation design. Monitor rock fragmentation during mining to optimize crushing processes.
Agriculture and Agronomy:Determine soil texture to guide irrigation and fertilization strategies (e.g., clay soils retain water better than sandy soils). Study soil aggregate stability to assess fertility and erosion resistance.
Construction and Civil Engineering:Test aggregate sizes for concrete and asphalt mixtures, ensuring compliance with building codes (e.g., 4.75mm sieve for fine aggregate). Screen backfill materials to prevent settlement in roadbeds and foundations.

The use of standard soil sieves runs through many fields from basic research to engineering practice. Its core role is to achieve accurate analysis and application regulation of soil properties through particle classification, providing a scientific basis for decision-making and practice in various industries.









